
Hardware I
 Content of the lesson:
Content of the lesson:
- Case
- Power Supply
- Motherboard
- Processor
- Operating Memory - RAM
Hardware
This term comes from an older English word which meant iron goods. It represents all physical equipment inside a computer which you can touch. Hardware is a set of electronic and electromechanical items which are connected to each other. It is something like a puzzle where every part has its purpose and all parts create one functional unit.
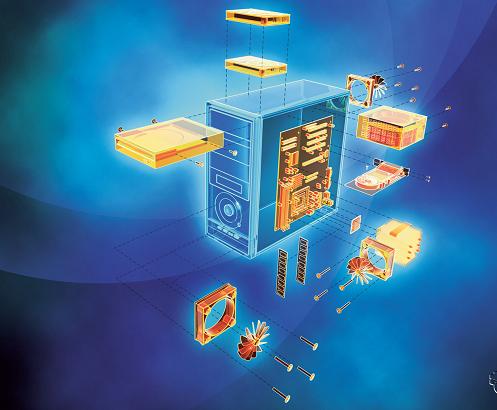

Computer (source: www.askdrtech.com)
Computer Case
The computer case is used to cover all other parts of hardware. They can be placed into it, attached on their places and connected to each other using cables. Several items are connected straight to the motherboard. Then the case is closed and the air flow system can work properly - each computer produces heat which has to be taken out of the case.
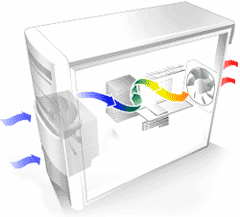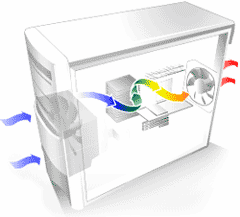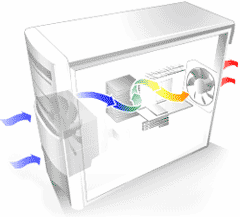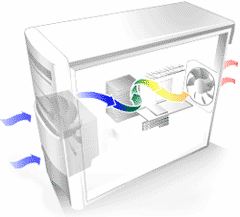
Air flow system
(source: programujte.com)
A computer case usually has buttons for power on and restart on the front side. You can also find control lights which signalize that the computer is turned on (green color) and that a hard drive is working (red color). USB ports are commonplace as well as ports for headphones and microphone. The rear part of the case is adapted so ports from the motherboard and additional cards inside the case are accessible. Motherboard and additional cards have ports (interfaces) which can be used to connect an external device. Cases have holes which are used for ports from motherboard and cards. These holes are usually covered at first to prevent the dust from getting into the case. You can uncover them in case you need them.

Computer case (source: cgi.ebay.co.uk)
Types of Cases
- Desktop - a horizontal case. A monitor is usually
placed on it.

Desktop (source: support.gateway.com) - Tower - a vertical case which is usually placed next to the monitor, under a table on the floor or into a prepared partition of a table.
- Bigtower - The biggest type of computer case, used especially for servers
- Middletower - Usually used for computers at home.
- Miditower - Usually used for computers at home.
- Minitower - Usually used for office computers.

Towers (source:
www.wikio.co.uk,
www.acetech.co.nz,
www.bj-computers.co.uk,
www.ccltechnologysolutions.com)
Power Supply Unit
This part supplies electric power to every part of the computer, nothing can work without it. AC voltage (value 230V, frequency 50Hz) is brought to the power supply unit from the electric network. The power supply unit has to adjust it - it converts it to DC voltage of different values (3,3V, 5V, 12V) because each component requires different voltage. Components then use this adjusted voltage or adjust it separately.
Standards of Power Supply Units

Power Supply Unit (source: www.digicomp.co.za)
- AT - This is an older type which had two supply connectors. The voltage of 5V and 12V was brought to motherboard using this unit. Turning the computer on and off was solved using a network switch.
- ATX - This type brings also voltage of 12V, 5V but also 3,3V to motherboard using only one connector. Computers are turned on and off from the motherboard which allows you to turn the computer off with a software (by clicking on "Shutdown" the computer is turned off, you do not have to use the switch).
- ATX 12V - This variant is extended by a 4pins connector with voltage of 12V. This change was caused by a huge load on the 3,3V branch.
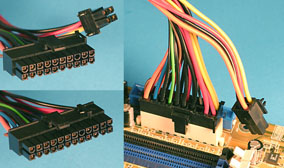
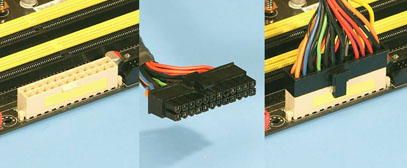
- ATX 12V 2.0 - Contains the new 24pins Main power connector.
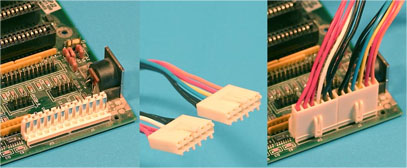
AT Connectors (source: www.playtool.com)
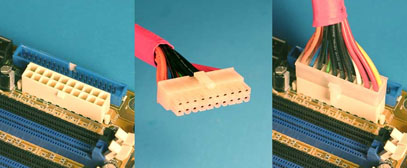
ATX Connectors (source: www.playtool.com)
Usage of Single Voltage Values
- +3.3V - powering the AGP port, also the chipset at cheaper motherboards, power for processor core
- +5V - control parts of disk drives, powering ISA buses, source of power for I/O part of processor (also chipset) and for several parts of motherboard (keyboard etc.)
- -5V - accessible on the ISA bus, this voltage was used by older frequency generators
- +5V SB* - auxiliary source for turning ATX unit on and for wake-up of computer
- +12V - power parts of disk drives, ventilators, serial ports, PCI (sound and measuring cards) accessible on the ISA bus
- -12V - serial port, PCI (sound and measuring cards) accessible on the ISA bus
source: Power Supply Units in PC
Performance of Power Supply Unit
Each part of computer needs a particular power and takes it from the power supply unit. The unit has to offer enough performance and its maximal value cannot be exceeded by the components. You can use several calculators to compute the required performance for your computer.
calculator for computing the required performance
Computers require a lot of energy but the consumption is not constant. In changes according to the usage of the computer. Most of components can save power by switching to standby mode if possible. In case that a computer is turned on and does not work, the consumption can be around 100 W. However, if you use it fully, it can be increased up to 500-600 W.
Motherboard

Motherboard (source: www.build-gaming-computers.com)
Motherboard is a part of computer which connects many components and controls the communication between them. To control the communication it uses so called chipset and usually two chips (integrated circuits) called north and south bridges. The connection of components is solved by buses (coppery tracks on the motherboard). To simplify we can say that a motherboard is the blood circulation of each computer.

Motherboard (source: www.tp-smith.co.uk)
- North bridge - Also called a system controller. This chip is closer to the processor because it controls fast movements of data. It controls fast data transfers between key components of computer. It is connected to FSB bus and controls the whole work with the other parts of the motherboard. It is also connected to AGP bus and the frequency of AGP bus is derived from the frequency of FSB because both sides use the same frequency generator. The north bridge is also connected to the bus of memory modules.
- South bridge - It is connected to additional peripherals. Its parameters are essential for the maximal transfer speed of hard drives, USB and more ports on the motherboard. It also provides the BIOS services.
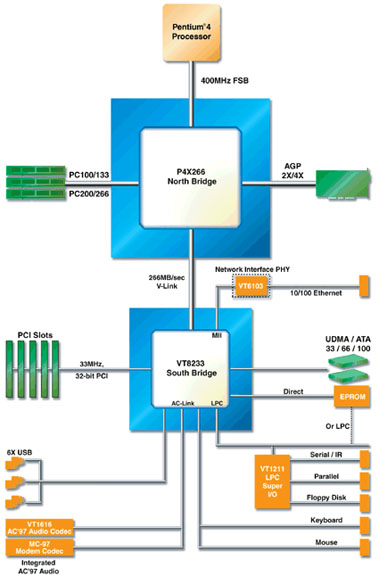

Motherboard (source: ixbtlabs.com,
techreport.com)
BIOS (Basic Input-Output System)

BIOS (source: www.neowin.net)
This small chip is used as an intermediate part between hardware and software. There is a special program saved inside it which contains for example instructions for launching an operating system. BIOS allows you to use several settings of motherboard or components which are connected to it. These settings are saved to another chip (CMOS) which is powered by a small battery. In case the battery discharges or you remove it, all settings will return to default values.
BIOS (source: www.washington.edu)
There are also connectors, socket, slots and ports on the motherboard.
- Connector - This component is used for mechanical and electronic connection of cables. This connection can be separated without any equipment.
- Slot - Long component which allows you to plug
cards
- ISA - These slots were used in the past for connecting graphic cards and 3D accelerators. They were also used for connecting sound and additional cards. The width of data flow is 16 bits.
- PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect, PCI Standard) -
Very used slot which was invented by Intel Corporation. It is
independent on the processor because it does not communicate with it
straight but using a bridge circuit. Its frequency is 33MHz and
theoretical data throughput 264MB/s. The data transfer is parallel. You
can often see it together with slots ISA (in case of reverse
compatibility). This slot is not usable for current graphic cards
because of low data throughput and started being replaced by AGP slots.
However, both variants nowadays are being replaced by PCI Express slots
which allow a serial transfer.
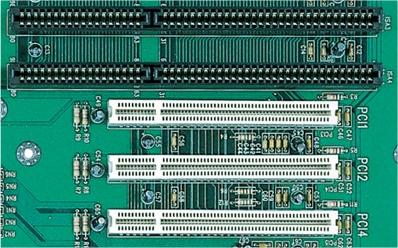
ISA (above) a PCI sloty (below)
(source: www.garethjmsaunders.co.uk)
- AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) - This is a slot developed for graphic cards. Its data throughput for example at AGP 4x is around 1GB/s. AGP is an adjusted PCI because several control signals are similar (the same number of cables as for PCI is used for transfers in address and data part). This slot allows a direct connection between graphic card and operating memory. Textures can be stored in operating memory and do not have to be transferred to local memory of graphic card before drawing them as in case of PCI connection. Similarly to PCI, AGP is independent on the processor because of the bridge circuit. There are several versions with different speed rates but the speed rates have to be supported by the motherboard.
- PCIe (PCI-express) - You can see a mark 3GIO = 3rd Generation I/O. This slot was developed to remove problems of PCI and AGP. It is a highspeed interface used not only for graphic cards but also for other modules. PCIe works on frequency 2,5GHz and in 32bit mode it can transfer data using a theoretical speed 8GB/s in one direction, in 64bit mode 16GB/s and in 128bit mode the speed can reach 32GB/s. It has support for so called Hot Plug/Hot Swap which allows you to remove cards without turning the computer off. These slots are connected with the south bridge on the motherboard; slot for graphic card is connected to the north bridge.
- Socket - This is a square component with many
small holes for pins (legs) of a processor. It is a slot designed only
for the processor. This component is used for its mechanical attachment
and electrical connection with the motherboard.
Socket (source: www.hardwarezone.com.au)

Connector (source: www.tomshw.it)
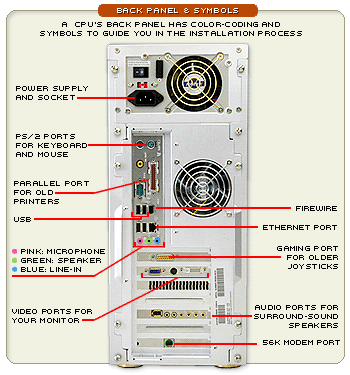
- Port - You can connect any device using a cable to this interface. Usually you can see ports on the rear side of case where ports are available. However, several cases also contain ports on the front size (for example USB).
- LPT - Parallel interface also known as PRN or Centronics. It was used for printers.
- COM - Serial interface also known as RS 232. It was used for modem or mouse.
- PS/2 - Serial interface designed for connecting a mouse of a keyboard.
- USB (Universal Serial Bus) - Serial universal interface for connecting any device. It replaces the previous examples of ports. A great advantage is the possibility to connect and disconnect devices while the computer is running. Very fast transmit speeds.
- FireWire (i.Link nebo IEEE 1394) - Serial interface for connecting a device to a computer. It replaces the previous SCSI connection. This interface is being used for connecting digital cameras, external hard drives or optical drives. It is not as spread as USB and will probably never be.
- VGA (Video Graphics Array) - This is an interface for connecting a displaying device (monitor, data projector to a computer).
- DVI (Digital Visual Interface) - Similar to VGA - used for connecting a computer with a displaying device. This interface was developed to transmit non-compressed digital video data.
- RJ-45 - Used for connecting Ethernet cable from a network of from the Internet.
- Audio ports - Speakers, microphone or external audio devices can be connected here.

24pins
connector (source:
nl.coolermaster.com)
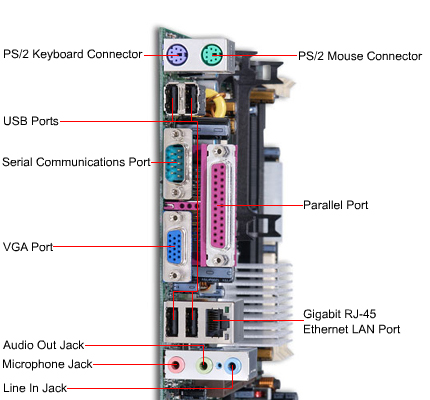
connectors on the motherboard (source: www.techiwarehouse.com),
rear panel of a computer (source: asia.cnet.com)
Central Processing Unit
This component is also being called as the Central Processing Unit or CPU. It is a part of computer which computes orders, processes instructions and commands of programs and manipulates with data. We can say that the processor is a brain of the whole computer. It is a small integrated circuit which consists of millions of transistors. We can say that the performance of computer is quite dependent on the processor. The most known producers are Intel and AMD.
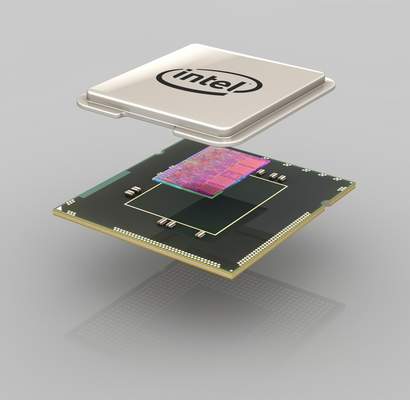

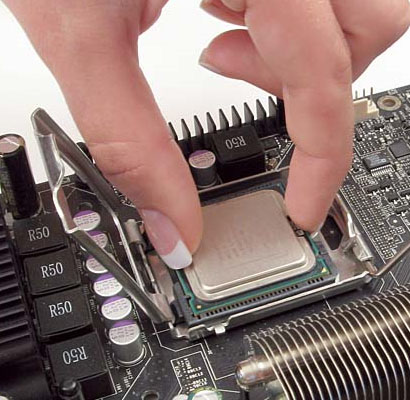
Processor (source: dmnvinod.blogspot.com, techreport.com)
Processor Parameters
- Clock frequency (GHz) - This parameter sets how fast the processor can process data and how fast it can do several calculations or operations with it. It is measured in GHz nowadays which means billions of operations done each second. At the end of 70s processors of type 8086 had clock frequencies around 4,77MHz. In the middle of 80s the processors of type 80386 had frequencies around 33MHz. Intel managed to reach the frequency above 5GHz. However, a higher number does not mean a faster processor. It also depends on the architecture. For example Intel Core P4 1,8GHz is much faster then AMD Athlon 64 3000+ (frequency 1800MHz).
- Cache (kB, MB) - Cache is a buffering memory which is used for storing data which are being used. This memory is very fast and the access time to it is minimal. The bigger cache, the faster work. You can imagine it as your table where you seat. There are several books on it. You need these books for your job. You work and need to find information from these books. You take the book and get the information. The table is a very fast variant. In case you did not have a table you would have to go to library every time you need information which would be much slower. The library represents the operating memory RAM.
- Number of cores (1, 2, 4, 8, ...) - This means a process of integrating more processors into one chip. This solution was forced by physical principles. The result is that you can get much more performance when creating a single-core processor using this technology.
Moore's Law
This is an empiric rule from 1969 from one of the founders of Intel Corporation (Gordon Moore) which says that approximately every 18-24 months the performance of computers is doubled. This rule is functional because of the miniaturization process (more transistors at smaller area) but is not infinity so companies which develop processors will soon reach a limit which will stop the development because of physical principles. You can see the curve which illustrates the density of transistors on a silicon plate in the following graph.
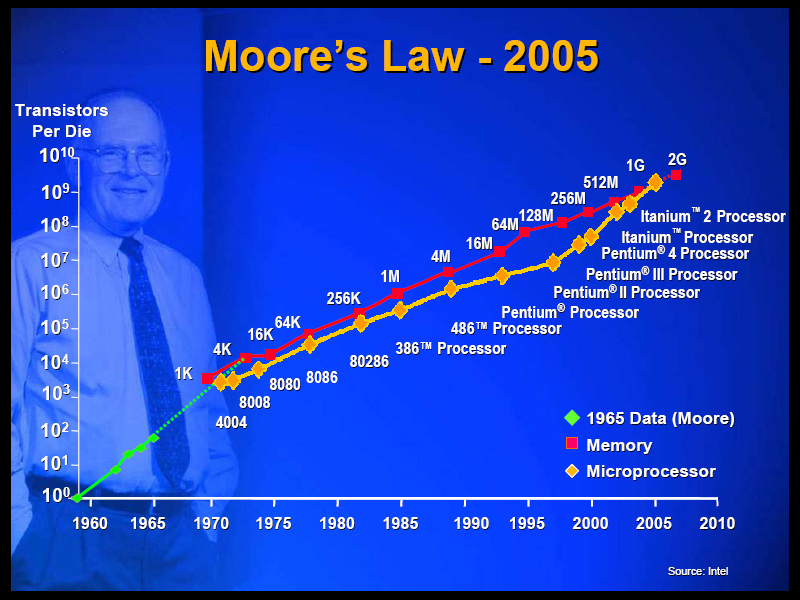
Moore's Law (source: www.ieee.org)
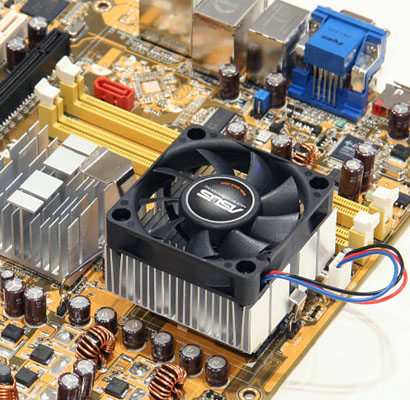
Cooler
This component is being used for taking the heat away from processor while processing instructions.
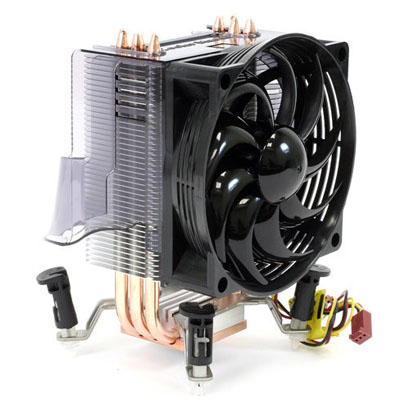


Cooler (source: www.xtremesystems.org, techreport.com)
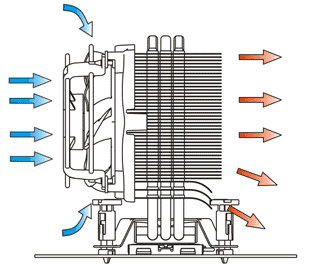
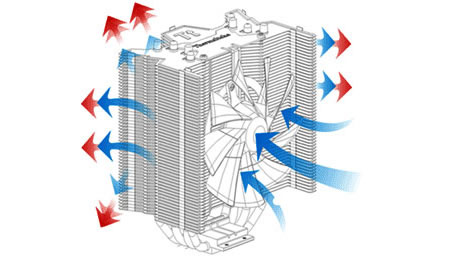
Cooler (source: wccftech.com, www.fareastgizmos.com)
Memories
Memories are components which can store a particular amount of data. The amount depends on the capacity of the memory which is being measured in Bytes. Memory consists of fields and every field has its unique address (a number which identifies the field). Fields are of the same size and one concrete field is being called as the smallest addressable unit.
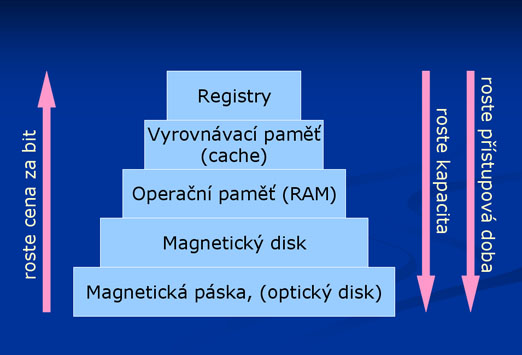
Hierarchy of memories (source: citel.spsbv.cz)
- Internal (operating) - This type is usually imagined when somebody hears the term "memory". This memory is inside a computer connected to the motherboard via a concrete interface. It is a plate which consists of area circuits and electronic devices (semiconductors, integrated circuits). It needs electric power to function properly, otherwise all content is lost. It is used to store data which are being currently used - temporary data of a launched program etc. Temporary data from processor are saved into this memory or loaded from additional memories because this memory is very fast, much faster than external memories like hard drive.
- External (peripherals) - An external memory means a hard drive, optical drive, USB disk etc. It is a device where data is stored for a long time and where it remains after removing the power supply. These memories are realized using a magnetic or an optical principle. Compared to the internal memory these memories are much slower, even the fastest ones are 1000x slower than the internal ones.
Operating Memory RAM
The RAM memory (random-access memory) looks like the plug-in modules which are being connected to slots on the motherboard. You can have one module or more modules (there are more slots on the motherboard). In that case, the capacities are summed.

RAM (source: www.digicomp.co.za)
- Static (SRAM – Static RAM) - Saving data using properly connected transistors which create a bistable flip circuit. Data is stored until the power supply is removed. This is the fastest type of memory but has large power consumption if busy. You can find it at processors as the cache memory.
- Dynamic (DRAM – Dynamic RAM) - Data is stored using
a capacitor which can be charged or discharged. This method of creating
RAM memories is easier and cheaper but the capacitor cannot remain
charged for the whole time when the power supply is connected. Data is
removed after reading it so a recovery is needed. Recovery is done after
reading any segment of the memory which makes the reading process 1,5x
slower than the writing one.

RAM (source: www.tomshardware.com)Division of DRAM memories according to the modules
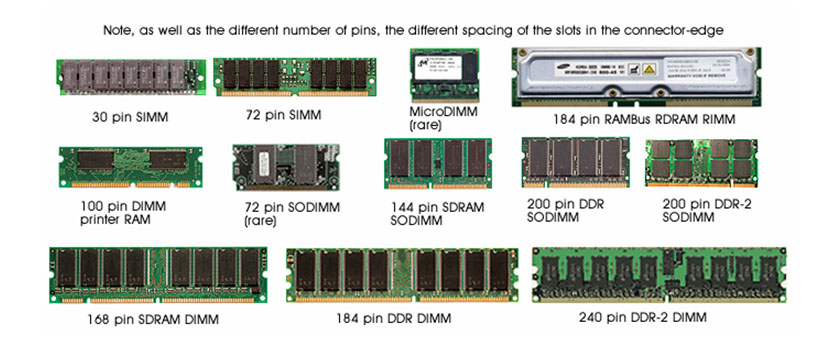
- SIMM modules
- DIMM modules
- RIMM modules
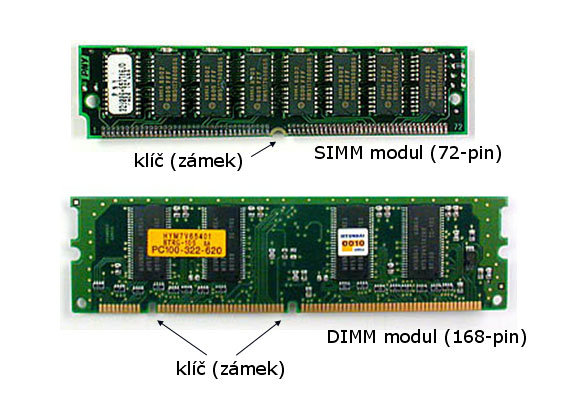
Division of dynamic RAM memories
- SDR SDRAM (Single Data Rate) - Older memories of type DIMM. They are sometimes wrongly marked as SDRAM. They have 168 pins, two keys (notches) and the capacity is between 32MB - 512 MB, speed 66-133MHz.
- DDR SDRAM (Double Data Rate) - Newer types of memories of the type DIMM. They have 184 pins, one key (notch) and the capacities are from 182MB to 2048 MB.
- DDR2 - a new generation of DDR, 240 pins, higher frequency
- DDR3 - a new generation of DDR, 240 pins, higher frequency
Animation (motherboard, processor, operating memory)
Additional Texts
- http://pctuning.tyden.cz/hardware/skrine-zdroje-chladice/14375-pocitacove-skrine-a-jejich-evoluce?start=2
- http://dmnvinod.blogspot.com/2009/07/from-sand-to-cpu-how-intel-makes-i7.html
- http://www.root.cz/clanky/interni-sbernice-pci-express/
- http://www.dancetech.com/article.cfm?threadid=156&lang=0
- http://www.21stoleti.cz/view.php?cisloclanku=2004052112
- http://www.svethardware.cz/art_doc-6A0605869C2AC5DFC1257206006DCCFA.html
Questions
- What is hardware?
- What is the purpose of each motherboard?
- What is BIOS?
- Which important parameters of processors do you know?
- What is the purpose of RAM memory?